Wireless Enterprise Authentication: 802.1X
The frequency of cyberattacks is high, and as a precautionary step, selecting the appropriate cybersecurity protocol has become a top priority for businesses. Each company may have varying verticals, target markets, and strengths of employees; however, they share the primary objective of ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of their corporate data to thwart any unauthorized access, modification, or destruction.
This article will delve into the logistics of setting up and running Wireless Enterprise Authentication, emphasizing the significant forms of Wi-Fi security protocols and which fits best for your business needs. When choosing wireless equipment for large organizations, having a comprehensive understanding of Wi-Fi security is critical, and this article offers just that.
What is Enterprise Authentication?
The Enterprise Authentication Service is a centralized authentication platform that verifies user identity across multiple enterprise applications. When end-users input their credentials into an application utilizing the Enterprise Authentication Service, the application initiates communication with the Authentication Service to authenticate their identity.
Eliminating the need to store password files on each company’s application server increases security. In addition, it helps cut down on costs by consolidating the administration of user credentials.
How Is It Different From Personal/Individual Authentication?
Both authentication mechanisms use strong encryption called AES-CCMP to protect data transmitted over the air. The primary differences between different security types become apparent in the authentication stage. IEEE 802.1X is the basis for the enterprise-level security provided by WPA2 Enterprise, while WPA2 Personal is a pre-shared-key (PSK) variant of WPA2 intended for domestic usage.
Although WPA2 is intended for usage in both homes and businesses, WPA2 Enterprise is exclusively tailored to the needs of companies.
Considerations for Enterprise Network Security
Please take into consideration the following factors to guarantee optimal security for your corporate network.
Security for Endpoints in the Internet of Things
Endpoint security is a critical aspect of ensuring the security of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. It is imperative to implement robust security measures to protect endpoints from potential cyber threats.
Mobility for IoT Devices
The surge in connected devices has led to a significant increase in the demand for wireless internet access. As per the analysis conducted by Gartner, the count of Internet of Things (IoT) endpoints in the business and transportation sectors is expected to reach 5.8 billion in the current year.
Business-Grade Security Applications
Installing and maintaining enterprise-grade security software on any company-owned devices and any employee equipment as part of a BYOD program is crucial in the fight against the security threats posed by the Internet of Things.
Network for Wireless Internet Access by Guests
Creating a guest Wi-Fi network is another strategy that has proven successful for certain businesses. Guests and visitors can only use the internet; your internal network and its resources remain hidden. Most importantly, they won’t inadvertently expose your systems to viruses or otherwise endanger your data. Thus, the strong business network is shielded from unwanted visitors.
What Are WPA Protocols?
In 2003, the WPA protocol was introduced as a more secure alternative to the less reliable WEP protocol for wireless networks. The WPA protocol is considered more secure than WEP due to its utilization of a 256-bit encryption key, a significant improvement over the 64-bit or 128-bit key used in the WEP protocol. WPA is a wireless network security standard developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance.
WPA operates in both enterprise and personal settings through separate modes. WPA-EAP is the newest enterprise mode, requiring a robust authentication method called 802.1X. WPA-PSK, the most recent personal mode, employs a secure handshake based on Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE). In the enterprise setting, customers must establish a secure connection with an authentication server before entering their credentials.
In the sections below, we will compare the WPA authentication protocols in different modes:
- WPA2-Enterprise
- WPA3-Enterprise
- WPA2-PSK
- WPA3-PSK
WPA2-Enterprise
One of the requirements for implementing WPA2-Enterprise is installing a RADIUS server, which is required to verify users before providing them with network access. Various EAP systems, which follow the 802.1X policy, drive the authentication procedure. To join a network, a device must first go through an authentication process establishing a private, one-to-one tunnel.
When X.509 digital certificates validate authentication, the WPA2 (Enterprise)-RADIUS combo offers maximum network security. Therefore, while configuring the web, utilizing the most secure authentication procedures possible makes sense, mainly because an 802.1X authentication server is necessary for WPA2 Enterprise.
WPA3-Enterprise
WPA3-Enterprise is an update to WPA2 that will ultimately replace it. This solution delivers a secure wireless network for businesses using 192-bit encryption and the 802.1X security standard.
Furthermore, a more robust data encryption technique is now available: WPA2-PSK
A wireless network that employs WPA2-PSK, or Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 Pre-Shared Key, utilizes a shared password for all users to ensure security. In network security, employing a singular password for Wi-Fi access can be considered secure, albeit contingent upon the end-users’ trustworthiness level. Due to its security vulnerabilities, WPA2-PSK is deemed an insecure encryption technique.
To maximize security, companies should ideally use WPA2-PSK for home networks or coffee shops.
WPA3-PSK
WPA3-PSK is an improved form of PSK that increases security by strengthening the authentication process. One method leverages Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) to thwart brute-force dictionary attacks. The need for user interaction in each authentication attempt severely hinders brute-force attacks against the protocol.
Is 802.1X & WPA2-ENT the Best Solution?
802.1X provides an authentication mechanism between a RADIUS server, such as an access point (AP), and client devices, such as laptops or smartphones, connected to the network via a wireless connection.
The 802.11 standard also describes how communications can be encrypted between these two components using WPA2-Enterprise, which is based on AES encryption technology and is more secure than any previous version of the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) protocol family.
WPA2-Enterprise Protocols
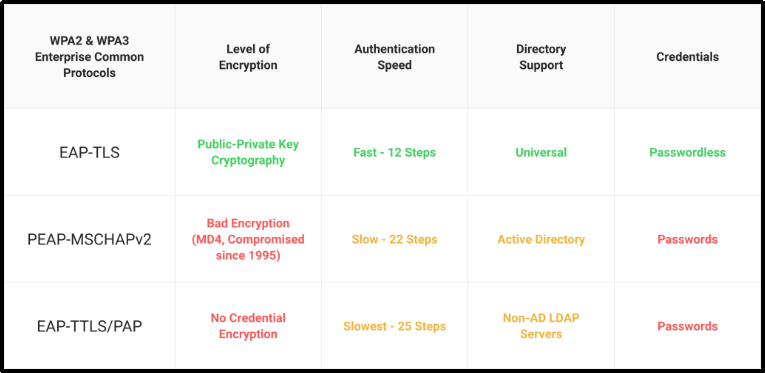
EAP, called Extensible Authentication Protocol, is a commonly utilized authentication method for wirelessly transmitting client data via the 802.1X protocol. There are many different EAP techniques; however, only EAP-TLS enables certificate-based authentication, which is the gold standard for authentication. This is because all other EAP methods utilize the EAP tunnel to transport information via an encrypted channel.
How Do You Deploy WPA2-Enterprise & 802.1X?
The authentication of wireless clients over an enterprise network requires an 802.1X RADIUS server. By enforcing user authentication, keeping activity logs, and implementing access control policies, Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) helps keep wireless networks safe.
The necessary hardware for 802.1X deployment is minimal. If you already have access points and unused server space, you likely have everything you need to implement secure wireless. Some access points already have the necessary 802.1x software installed, eliminating the need for a server entirely (though only for the smallest of small deployments). The quality and simplicity of 802.1x is essentially a function of design, regardless of whether you buy professional solutions or construct one using open-source tools.
To read the steps involved, refer to this article.
How Does 802.1X Authentication Help Your Business?
When it comes to safeguarding a network, authentication is paramount. Preventing potential disasters like hackers breaking into your network is a top priority. If a company’s defenses are weak and its service providers don’t have sufficient authentication measures, it might face severe fines and a damaged image in global markets.
Let’s examine why firms must swiftly improve their identity authentication:
1. Securing consumer identity is crucial now more than ever before.
2. GDPR and CCPA privacy standards are growing increasingly rigorous.
3. While gathering user information, developers face challenges with identity verification.
4. Customers expect a high-quality experience with your platform from the first interaction.
5. Businesses may establish credibility with customers by tailoring their experiences.
Why Should Your Organization Choose WPA2 Enterprise?
WPA-Enterprise is better for business or enterprise settings because it has more security features. Apart from the apparent enhancements to IT security, there are some immediate benefits, which are:
Leavers and Starters: Wireless network access may be promptly revoked when a person quits the company. Every firm would have a significant administrative burden if they used a PSK since every user device must have the key updated and reconfigured. Fortunately, this seldom occurs.
Accountability and Auditing: Thanks to user logins, you can track who accessed what on the network. Users’ activities on the WiFi network may be tracked with the help of logs. While this is technically doable with WPA-Personal (through MAC addresses), it could be smoother.
Authorization: A user’s entry to the network is protected by Authentication, but their actions while inside are subject to Authorization. The resources available to them, the hours they may use, and so on are just a few examples. Although the two are similar, authorization controls provide more control across a connection.
Convenience and SSO (Single Sign-On): SSO makes network access seamless and familiar to users. Users can easily use their same Windows credentials to access the WiFi network. Granted, you need to ensure your business has a robust password policy.
Here’s the million-dollar question:
As a business owner, do you share a single Wi-Fi password with your staff, from the janitor to the CEO?
Probably not.
But a recent report from a company that makes password managers showed that about 40% of companies still manage passwords by hand. The report also showed that over half of companies let employees watch how they use passwords. This lack of security is a surprise, but not. 45% of the people surveyed said that managing passwords makes them less productive.
Even after years of news about critical corporate data being lost by hackers due to inadequate password systems, most business owners still do not prioritize password management. Despite how often IT experts emphasize using solid passwords, most users still need help understanding.
The most likely reason is to protect the company’s image, which will harm customer loyalty to the company’s product or service due to recent data breaches, leading to lower sales and a worse return on investment. Even though there may be customer service issues and environmental implications, companies often lose consumers when consumer data is lost.
That’s where we come to the rescue!
SecureW2’s Solutions for Managed Devices
Previously, one of the most challenging aspects of implementing digital certificates was getting them onto all of your network’s devices. This is no longer the case, thanks to our powerful certificate enrollment gateway, which integrates with all significant MDMs such as Workspace One, Jamf, Intune, and MobileIron. In addition, by removing the chance of misconfiguration, SecureW2’s JoinNow MultiOS allows you to safeguard and securely access your organization’s wireless network on unmanaged devices/BYODs.
Read how a Fortune 100 Giant Approached SecureW2 about migrating to the cloud and how SecureW2 simplified the transition to EAP-TLS by providing a turnkey solution tailored to businesses transitioning from on-premises to the cloud without requiring costly and time-consuming forklift upgrades. Want to hear more about our work? Check out the Our Customers Stories page.
SecureW2 also eliminates the need for significant infrastructure upgrades by providing a dependable certificate distribution and management method from distribution to revocation for all your controlled devices. To explore more, visit here.




