TACACS vs RADIUS: The Better Authentication Method
Organizations are looking at ways to protect their network as increased cyber attacks are infiltrating complex network systems. The rapid growth of artificial intelligence has also led to a steep rise in the number of complex attacks being attempted on organizational networks. It is becoming increasingly difficult for administrators to view the users and devices that access the network, making the role of Authorization, Authentication, and Accounting (AAA) pivotal.
TACACs and RADIUS are two pioneer AAA protocols that offer superior network security. They are designed uniquely, and this article will take you through a high-level comparison of the TACACs vs RADIUS and see which one best fits your organizational needs.
TACACs- A High-Level Analysis
The Terminal Access Controller-Access Control System (TACACS) is a network protocol developed for centralized and automated authentication, authorization, and accounting of network devices like routers, switches, and firewalls. In 1984, CISCO developed TACACS and released it as an open standard protocol. From then on, the TACACS protocol mainly functioned as a network control protocol and helped administrators set user access controls for devices, resources, and network applications.
TACACS uses a central server that authenticates users and controls their access to network applications. It also monitors their activities on their managed CISCO devices and the CISCO server. When prompted, a user provides his username and password and is verified against their existing details in the database. The user can access the network and applications based on his authorizations if verified.
The TACACS+ has superseded the TACACS and provides a more secure option with enhanced encryption, support for authentication mechanisms like two-factor and multi-factor authentication, and transmission control protocol (TCP) for better communication.
How Does The TACACS Protocol Work?
The TACACS functions on the client-server model, wherein a client (a remote server) requests to gain access to a network, and the TACACS server authenticates and authorizes the user to access the network.
- The remote access server first places an authentication request to the TACACS server.
- The TACACS server sends the access request packet to its database for verification.
- Upon verification of the user credentials, the TACACS server transmits the authorization to the remote access server.
- If the user can access the resource, the remote access servers grant or deny access based on the authorization message.
The TACACS+ can manage server options like attributes, define users, and control authentication services. These attributes can be set through the options section in the operation framework of a service, file name, and shared secret key. The next part of the file consists of a group of users and groups to control accounting, authorization, and authentication. The TACACs+ follows the user = username or group = user name and is succeeded by the single and multiple attribute pairs placed inside curly brackets.
An authentication process starts when the client initiates a TCP session. The TCP transmits attribute pairs to the server in a standard header format followed by a variable length parameter field. An AAA request is captured as a header and sent in a clear format; the rest is sent as a parameter. This ensures the parameter filed is encrypted for confidential, secure message transmission.
The TACACS variable perimeter provides extensibility and site-specific customization, and the TCP protocol provides a secure and safe delivery of the secret message. The server’s capacity, however, could be impacted by the format and protocol, as the format puts a load on the communication capacity of a server.
TACAS+ Use Cases and Benefits.
The TACACS+ is typically used in enterprise networks to access network devices, emphasizing scalability, security, and adaptability. Some routine use cases of the TACACS+ protocols include
- Authorizing Users For Remote Access-TACACS+ is used to authenticate users, typically in an extensive network, to access network devices, applications, and resources through a VPN.
- Authorizing Devices for Network Access- TACACS+authorizes only known network devices like access switches and firewalls to access the network.
- Validating Remote Access Server- TACACS validates various servers like the web and database servers to grant access to users on the network.
Benefits of TACACS+
TACACS+, the extensible version of TACACS, offers many benefits to an organization compared to the TACACS protocol. First, it is a more secure and centralized protocol for managing users and granting them access to a network. Some notable benefits of TACACS are listed below:
- Enhanced Security
- Scalable for growing networks
- Allows for centralized administration
- Enforces granular access control
- Provides data for accurate accounting
- Enhances Security
TACACS+ enhances security by supporting various Wi-Fi protocols like PAP, CHAP, and MS-CHAP. It also encrypts all the traffic between the user (client) and the server to safeguard any user credentials and traffic from vector attacks and unauthorized access.
- Scalable For Growing Networks.
TACACS+ has been designed to handle extensive networks with many users and devices. The TACACS+ is also economical, reliable, and provides ease of implementation. However, a TACAS+ network can only support CISCO’s NAS VPN, making it native to only CISCO-centric environments.
- Allows For Centralized Administration of Network Devices
The TACACS+ server allows for a centralized administration; a network administrator can look at all the users and devices from a single access point in a server. The centralized access makes it cost-effective and reduces admin complexity associated with controlling access on individual network devices.
- Enforces Granular Network Access Control
TACACS allows network admins to administer granular access control for users and devices. An organization can assign role-based, policy-based, and attribute-based access controls to users and devices by enforcing granular access controls. This ensures that only authorized users can access applications, resources, and data.
- Provides Data For Accurate Accounting
TACACS+ maintains records of user activities like their in and out times, applications, resources accessed, and any commands they have executed during their session. The data can be used for audit and compliance processes and troubleshooting issues during the session.
RADIUS- A High-Level Analysis
The Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, or RADIUS, is used widely as a network security protocol based on the client-server model. With the RADIUS protocol, clients like users and devices can place requests to access services from any location. RADIUS is user-friendly, effective, and scalable for growing businesses, thus emerging as an industry standard to attain the IETF standardization.
The mode of communication between a Network Access Server (NAS) and RADIUS functions is based on the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). The RADIUS authentication protocols are of utmost importance in the 802.1X architecture, where point-to-point protocol and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) are utilized. They perform the function of AAA.
- Authentication – matches user credentials to verify identity.
- Authorization – determines user permissions.
- Accounting – tracks user network resources.
How Does The RADIUS Protocol Work?
A Network Attached Storage (NAS) is typically a RADIUS client; the RADIUS server is a process initiated on a UNIX or Windows machine. The NAS client transmits user information to a specified RADIUS server and responds to the returned message. A RADIUS server typically receives requests to connect users, authenticate them, and then return the configuration details to the client for the requested service for a user. A RADIUS server can also mimic a proxy client to another RADIUS server or different kinds of authentication servers.
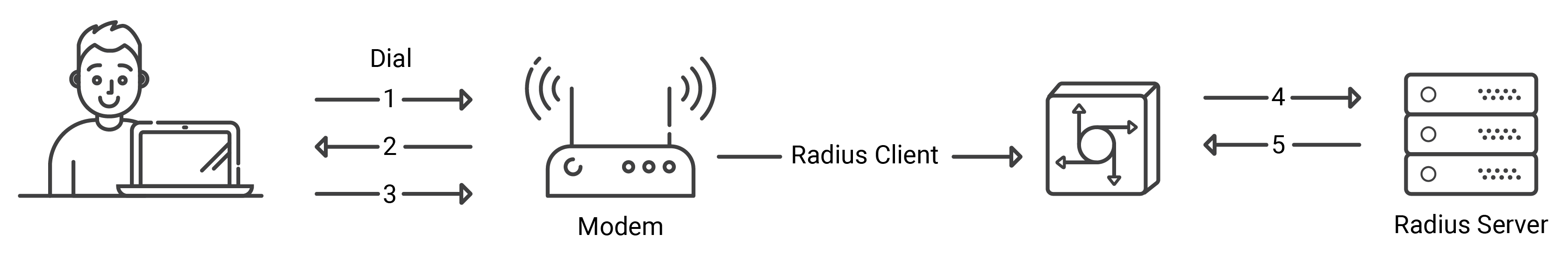
RADIUS Client Server and Dial-In user interaction
- A user places a PPP authentication request to the RADIUS Client, i.e., NAS.
- The NAS asks for credentials like the username and password in case of a Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) or challenge in case of a Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP).
- The user supplies the credentials that are asked for.
- The RADIUS client sends the encrypted credentials to the RADIUS server.
- The RADIUS server throws a response in the form of Accept, Reject, or Challenge.
- The RADIUS client provides access to services and user resources based on Accept or Reject parameters.
Benefits of RADIUS
RADIUS provides a centralized AAA control for users who wish to connect to a network and has been accommodative of various protocols and modern networks. Though the legacy AAA protocol still consists of on-premise servers, the cloud-based RADIUS authentication is slowly gaining popularity in modern network setups. Some benefits of RADIUS are the following:
- Provides enhanced security benefits
- Enables 802.1X using EAP-TLS Protocol for CBA
- Integrates with numerous IT infrastructures
- Makes Granular Control and Management Easier
- Provides Enhanced Security Benefits
RADIUS supports various Wi-Fi and authentication protocols that provide unique credentials to users instead of shared keys alone. RADIUS also supports MFA and digital certificate-based authentication for enhanced user and device authentication security.
- Enables 802.1X With EAP-TLS for Certificate-based Authentication
RADIUS enables 802.1X with the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) framework for authentication. The EAP protocol helps transmit authentication packets between two components with ease. The EAP framework consists of many frameworks, like the PEAP-MSCHAPV2, which supports password-based authentication, and the more secure EAP-TLS authentication, which supports digital 802.1X certificates.
- It integrates with numerous IT infrastructures.
Unlike on-premise setups, the modern Cloud RADIUS integrates with any IT system without needing a significant overhaul. You can add it to your existing infrastructure in layers for enhanced security. For example, you can divide your network into segments and enable level-wise authentication through digital certificates for crucial network resources, thus enhancing security.
- Makes Granular Access Control Easier
RADIUS makes it easier to see who and what has access to what resources through VLAN monitoring and segmented attributes. This RADIUS-specific feature makes it a standalone protocol, ensuring only authorized users and devices can access sensitive information and applications.
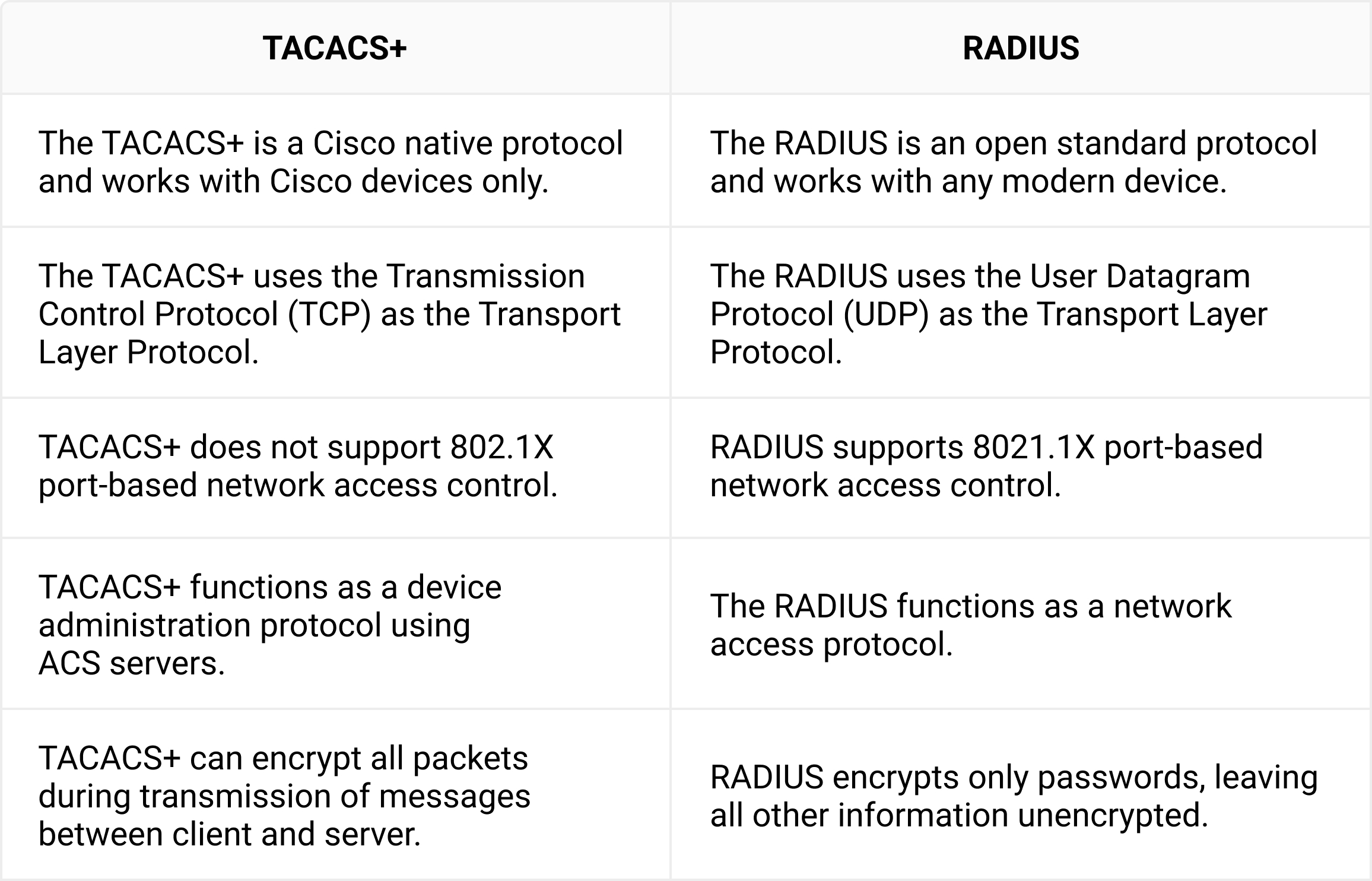
Difference Between TACACS+ and RADIUS
The most pertinent distinction between RADIUS and TACACS+ is that RADIUS is used to authenticate users to a network, whereas TACACS+ is used to monitor network devices like routers and switches. Here are some more differences between the TACAS+ and the RADIUS protocol:
TACACS+ or RADIUS- The Better Choice For Your Organization
The TACACS+ is a choice for industries with higher security demands like finance, security, and defense, where breaches are considered catastrophes. RADIUS provides easier integration and can be scaled to growing needs, unlike on-premise setups. It is the go-to choice for managing user access for educational institutions, internet service providers (ISPs), and small and mid-size enterprises with many users, managed devices, and BYODs.
TACACS+ and RADIUS have made a prominent case for being a superior network security protocol per industry standards. However, every organization has specific needs and may want to weigh their choices before you can opt for a protocol to secure your network. The RADIUS is the way forward if you are an organization looking for a simple, out-of-the-box implementation.
Suppose you are an organization with many devices, a mix of routers and switches that need to be secured, and also have to control user access for accounting purposes. Then RADIUS is the clear winner and a better choice.
Leverage SecureW2’s CloudRADIUS For Seamless Integration
As an organization with growing business needs, network security is getting cumbersome, and organizations are looking for robust, foolproof security solutions. As an organization standing at the crux of growth, weighing your security options before choosing is very important. The TACACS+, a Cisco proprietary protocol, supports Cisco network devices, making it a better choice for larger organizations with rigid in-premise setups.
You can safely switch to SecureW2s CloudRADIUS, a wholly cloud-based RADIUS solution that integrates with your existing infrastructure without needing an overhaul. Our PKI solution helps you distribute digital certificates at the click of a button through Managed API solutions so that your users and devices are securely onboarded without the risk of misconfigurations.
Click here for more on our cloud-based security solutions for your organization.