What is an AAA Server?
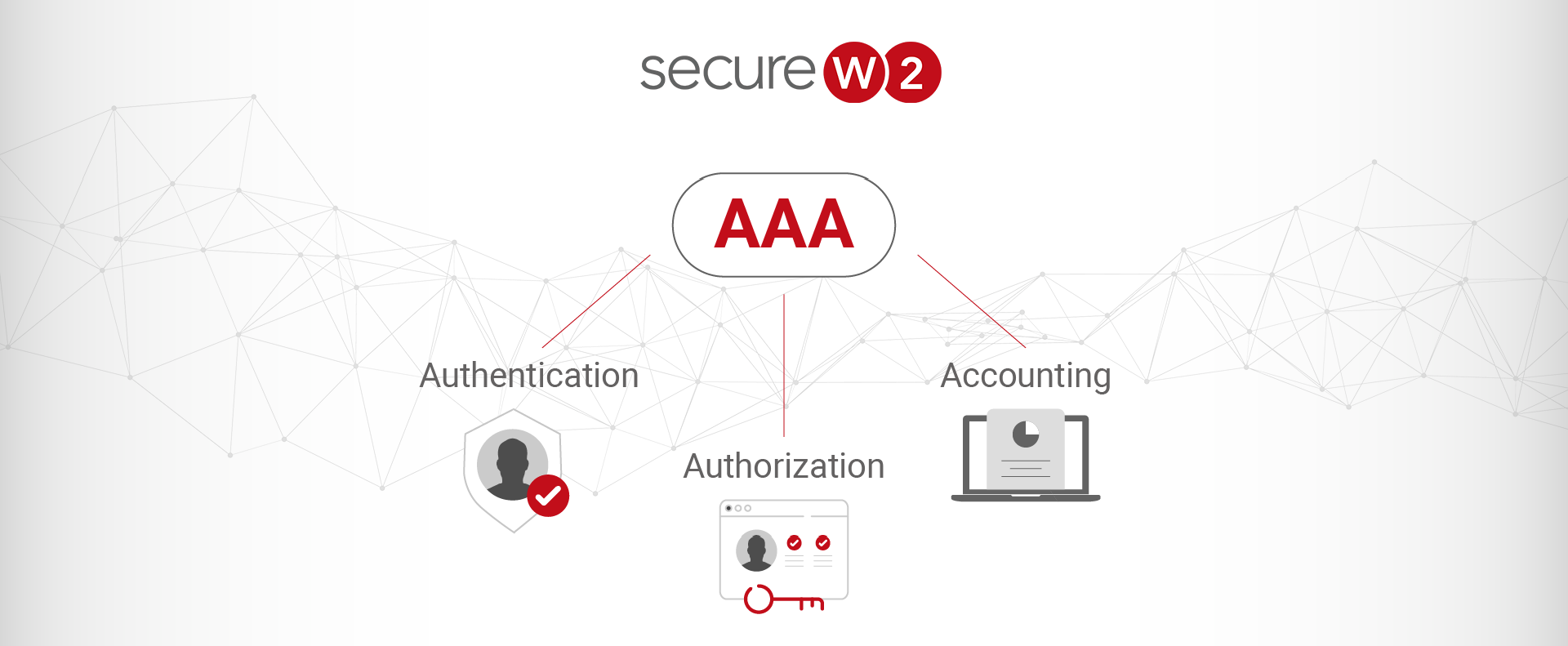
Securing network access and related equipment is very important in this modern era, where everything is connected to the internet. As organizations grow and their network infrastructure becomes more complex, access management and protecting critical assets and information becomes more challenging. This is where AAA servers help easily manage all of the infrastructure from a single pane of glass. AAA stands for Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting, representing the three fundamental pillars of network security and management.
An AAA server is crucial for network security and managing user access and authorizations. Authentication, authorization, and accounting servers ensure the protection of network resources by offering a centralized framework for authenticating and authorizing users’ access to specific resources. These servers play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data within a network.
In this article, we’ll provide a comprehensive understanding of AAA servers. We’ll also explore their benefits, how they are implemented, and what security protocols they use. Additionally, we’ll highlight Cloud RADIUS, a cloud-based managed RADIUS service of SecureW2 that offers advanced security features through passwordless certificate-based authentication. Let’s start it.
What Does AAA Server Mean?
We’ve already established our understanding that AAA stands for Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting, but how does it all translate into a practical solution for your network? An AAA server is a dedicated program that is the central point for managing these critical access control functions. These three functions form the backbone of network security by controlling user access and monitoring network activity. Let’s explore each component in a bit detail.
Authentication
Authentication is identifying a user or device before granting access to a network. It ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information and resources. This process typically involves validating user credentials such as usernames and passwords, but it can also include more advanced methods like biometric verification or digital certificates.
For example, when an employee tries to log into the company network, the authentication process checks his user credentials against a local database. If the credentials match, the user access is granted; if not, it’ll be denied. This step helps prevent unauthorized access and protect the network from potential security breaches.
Authorization
Once a user’s requests are authenticated, the next step is authorization. Authorization determines what resources and services are allowed to be accessed. It involves setting permissions and access controls based on the user’s role and responsibilities and the organization’s security policies.
For instance, a network administrator might have access to the entire network and all its resources. In contrast, a regular employee might only access specific applications and data relevant to his job. Authorization ensures that users can only access the information they need, reducing the risk of misuse.
Accounting
The final component of the authentication, authorization, and accounting server is accounting, which involves tracking and logging user requests within the network. This function records login times, session duration, the resources accessed, and any changes made. Accounting provides a comprehensive audit trail that can be used for monitoring, reporting, forensic analysis, and internal and external IT audits.
If a security incident occurs, logs can help trace the source of the breach and identify any malicious activities. Additionally, accounting data is valuable for compliance with regulatory requirements as it provides evidence of user access and security measures.
AAA servers provide a robust framework for managing network security by integrating authentication, authorization, and accounting into the system.
What are the benefits of an AAA server?
Authentication, authorization, and accounting servers provide several advantages that improve security, streamline management, and ensure regulation compliance. Here are some of the key benefits of implementing an authentication, authorization, and accounting server including:
Enhanced Security
An authentication, authorization, and accounting server’s primary benefit is enhancing network security. An authentication server ensures that only verified users can access network resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Furthermore, the accounting function provides detailed logs of user requests and enables security teams to detect suspicious behavior promptly.
In an enterprise environment, an AAA server can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. This centralized control helps protect against internal and external threats and the organization’s digital assets.
Improved Access Control and User Management
Authentication, authorization, and accounting servers simplify user access management by providing centralized access policies. This approach makes it easier to manage user permissions, especially in enterprise organizations. Network security administrators can quickly update access controls from a single point of view and ensure that policies are consistently applied across the network.
Security administrators can easily update or revoke access rights through the authentication server when an employee changes roles or leaves the organization. This streamlines the user management process and reduces the risk of outdated permissions.
Logging for Auditing and Compliance
The accounting function of an AAA server provides logs of user activities, which are important for auditing and compliance purposes. These logs contain login times, session durations, computer resources accessed data, and any changes made in user credentials.
This information helps organizations meet regulatory requirements by providing an audit trail of user activities.
Scalability for Growing Networks
It’s challenging to manage users when businesses grow and their networks expand. Authentication, authorization, and accounting servers can easily scale with growing networks and ensure that security controls remain effective even when users and devices increase in the network.
An organization experiencing rapid growth can rely on an authentication server to manage the influx of new users and devices without compromising security. The server’s scalability ensures access policies are consistently applied and security remains robust.
What is a AAA Virtual Server?
As organizations evolve more flexible and scalable IT infrastructures, virtual servers become increasingly crucial. An AAA virtual server performs the same tasks as a physical authentication server but within a virtualized environment. This means that software manages authentication, authorization, and accounting functions, making it easier to scale, configure, and maintain.
An AAA virtual server is referred to as a cloud-based AAA server. Deploying an authentication server in the cloud provides several advantages. The significant advantage of implementing a cloud-based AAA server is cost-effectiveness. It’s less expensive than traditional hardware solutions because it allows businesses to pay for only the computer resources they use. And can be managed globally for large infrastructures.
Cloud Radius by SecureW2
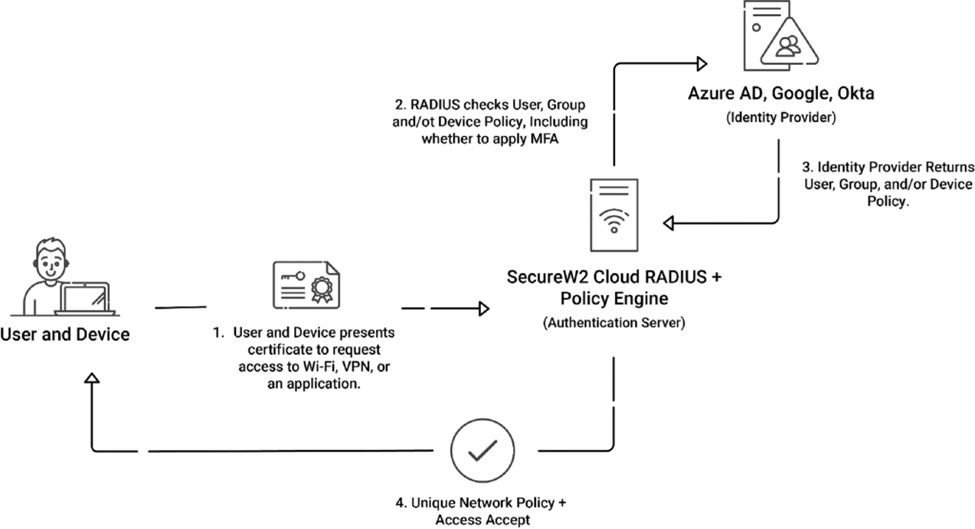
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS is a cloud-based authentication server. It’s a managed RADIUS server hosted in a public cloud environment such as Microsoft Azure. It provides advanced security and simplifies authentication requests. The key benefits of its implementation including:
- Cost Effectiveness: Cloud RADIUS by SecureW2 eliminates costly hardware requirements and maintenance and provides a cost-effective solution for network security.
- Scalability: It scales seamlessly with organizational needs and allows businesses to adapt network capabilities according to changing demands.
- Global Access: Cloud RADIUS enables organizations to implement secure, passwordless, and certificate-based authentication, which can be accessed from anywhere in the world.
- Integration with Existing PKI: You can seamlessly integrate it with existing Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) or create a PKI if it doesn’t already exist.
How Do You Implement an AAA Server?
Several steps are involved in implementing an authentication server. The following step helps you to implement an AAA server authentication authorization.
Step 1: Initial Setup and Configuration
Choose the authentication server program that best suits your organization’s needs. Some solutions are FreeRADIUS, Cisco Secure ACS, and Microsoft NPS for on-premises deployments. If you want to manage an AAA server authentication authorization from the cloud, you can choose managed services like SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS for cloud-based implementations.
Step 2: Install the AAA Server
Install the authentication server program on a suitable platform. For on-premises deployments, you can set up a dedicated server or virtual machine (VM). For cloud-based deployments, you can choose Cloud RADIUS, which is handled by the service provider.
Step 3: Configure Network Settings
Configure network settings for your AAA server, such as IP addresses, subnet masks, and gateway.
Step 4: Connect Network Devices
Configure network devices (e.g., routers, switches, wireless access points) to use the AAA server for authentication, authorization, and accounting purposes.
Step 5: Define Authentication Methods
Define which authentication methods, such as passwords, tokens, or digital certificates, you’ll use. Ensure that these methods are supported by both the AAA server and the client devices.
Step 6: Setup User Database
Configure the user database on the AAA server or an external directory service like LDAP or Active Directory. This local database stores user authentication credentials and other relevant information.
Step 7: Create User Profiles
Define user profiles and permissions for different user roles within the organization. For example, administrators may have full access to network resources, while regular users have access only to required computer resources.
Step 8: Configure Authentication Policies
Set up policies that determine how users are authenticated. This can include multi-factor authentication (MFA), password policies, and certificate-based authentication.
Step 9: Configure Authorization Rules
Define authorization rules that determine what network resources users can access once they are authenticated. This can involve setting up access control lists (ACLs) and role-based access controls (RBAC).
Step 10 Log User Activities
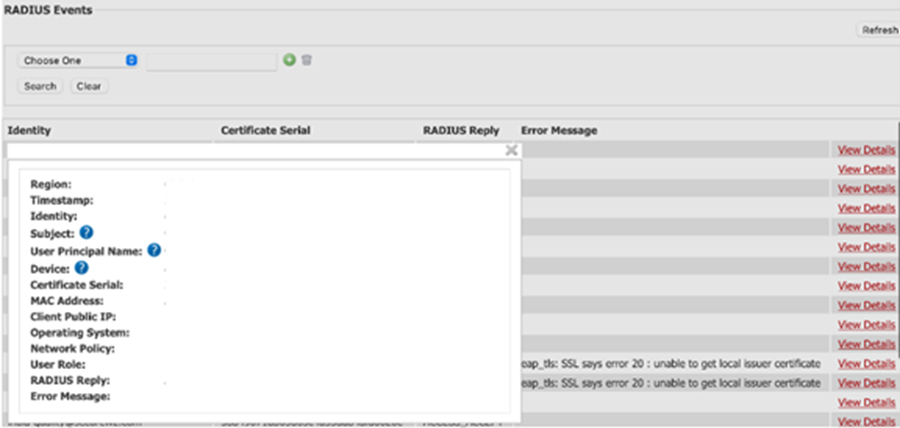
Configure the AAA server to log user authentication, such as login attempts, session durations, and resource usage.
Step 11: Configure Storage to Store Logs
Configure storage to store log activities. This can be on the AAA server itself or an external logging server.
Step 12: Setup Alerts and Reports
Configure the AAA server to generate alerts for specific events, such as failed login attempts or unauthorized access attempts.
What are the security protocols used by AAA servers?
AAA servers rely on robust security protocols to secure your network. These protocols maintain the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of network resources. The most commonly used security protocols for AAA servers are RADIUS, TACACS+, and Diameter. Each protocol has unique features and use cases, contributing to a comprehensive approach to network security. Let’s discuss how they protect your critical environment.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service)
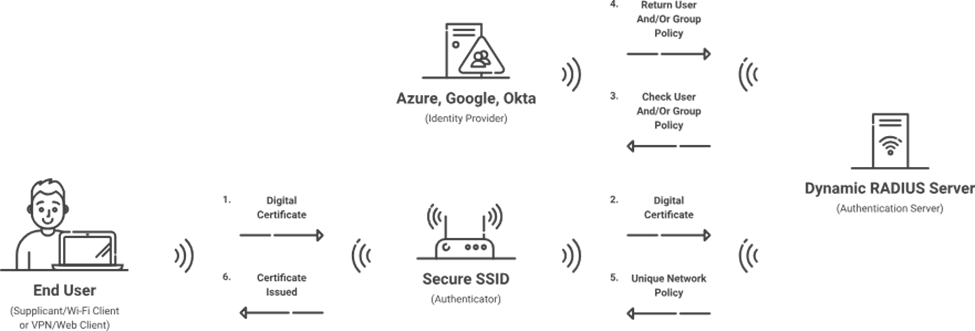
RADIUS is a frequently utilized authentication protocol, especially for enterprise environments. It was initially developed to authenticate, authorize, and account for users accessing dial-in services. However, it has since evolved in various network access scenarios, including VPNs, wireless networks, and Ethernet switches.
RADIUS operates as a client-server protocol where the client is typically a Wi-Fi access point, and the server is the RADIUS server. The client sends user credentials to the authentication server, which verifies the information using a database. If the credentials are valid, the authentication server grants access and applies the appropriate policies for user authentication. The authentication server also tracks user activities such as session duration, data usage, and resource access.
TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus)
TACACS+, developed by Cisco, provides centralized AAA services for network devices. It is popular in enterprise environments where device management and command-level access control are important.
TACACS+ operates as a client-server protocol similar to the RADIUS server. The client communicates with the TACACS+ server to authenticate users. It provides detailed control over user permissions, allowing administrators to specify which commands a user can execute on a device.
Diameter
Diameter is an advanced AAA protocol designed to address the limitations of RADIUS. It is often used in large-scale and next-generation networks like 4G and 5G mobile networks.
Diameter builds on the foundation of RADIUS but introduces several improvements. Its messages are exchanged between client and server to authenticate users, authorize access, and account for resource usage.
The selection of an AAA protocol depends on the organization’s requirements. RADIUS is commonly used because of its compatibility and scalability. TACACS+ is recommended for enterprise environments that require detailed command-level authorization, while Diameter is best suited for large-scale networks.
Manage Your AAA Server Authentication with SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS
AAA servers protect network resources by ensuring authorized access only. This article explored the basic concept of AAA servers, their benefits, and how they can be implemented on-premises and in the cloud.
If you want to deploy AAA servers in the cloud, SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS offers many advantages including cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ease of management. Cloud-based solutions eliminate the need for substantial upfront investments in physical hardware and allow organizations to pay only for the network resources they use. They also provide the flexibility to scale seamlessly as network demands grow, ensuring consistent performance and security.
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS is a powerful managed solution for organizations looking to enhance network security. With passwordless, certificate-based authentication features and seamless integration with existing PKI systems, Cloud RADIUS provides a comprehensive approach to managing network access in a secure, scalable, and cost-effective manner.
Visit our Cloud RADIUS to learn more and start your journey toward a more secure network today.