
802.1X MAC Auth for Devices Without WPA2-Enterprise Support
Securing network devices is crucial in today’s linked world to prevent cyberattacks. However, not all devices share an operating system that allows them to implement the prevalent 802.1X MAC authentication. Anything from smart home gadgets to hospital-grade medical equipment to specialized factory gear might fall into this category.
These devices may have limited functionality, but they nonetheless need extensive security precautions since they interact with the network and might be used as entry points by hackers. That’s where media access control (MAC) authentication comes in. It allows devices access to a protected network even if they don’t support WPA2-Enterprise.
Understanding 802.1X Authentication Using a MAC Address
What Is 802.1X Authentication?
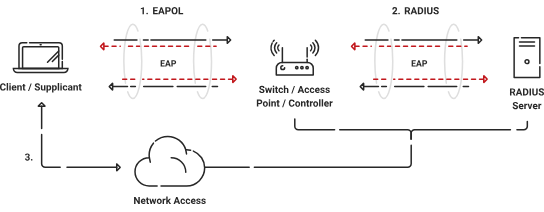
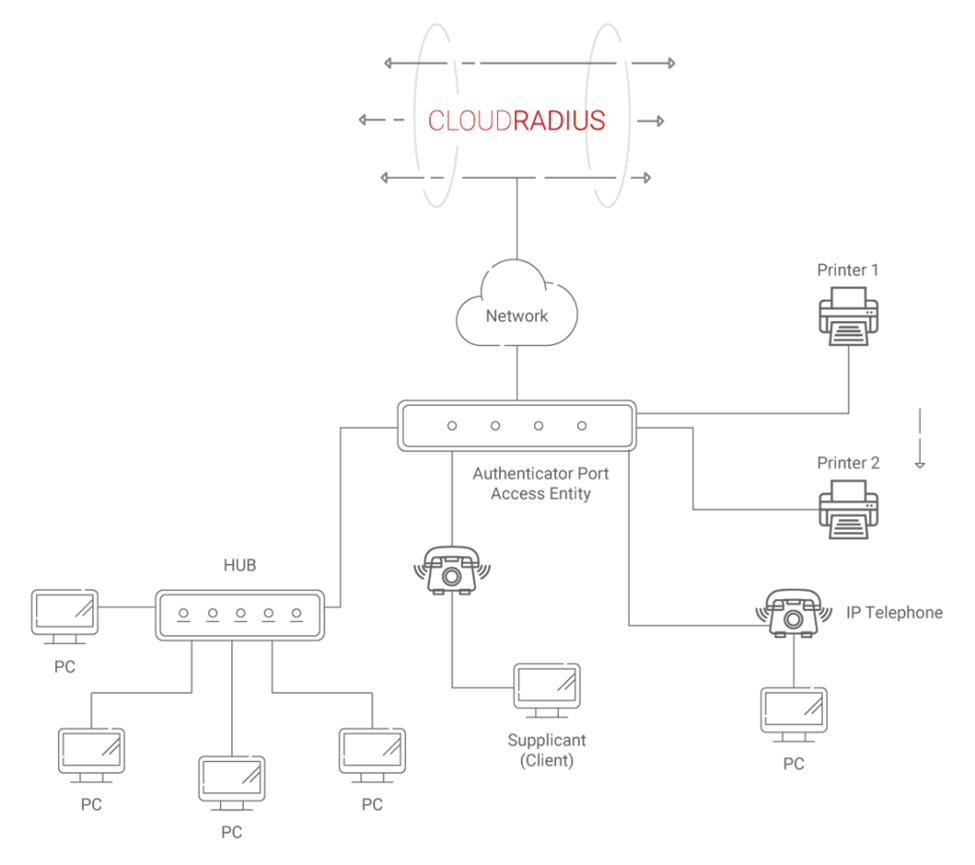
The 802.1X authentication protocol is extensively used because it verifies the identity of users before granting them access to a network. It offers a system for devices to connect safely by checking the validity of their authentication credentials or certificates with the help of an authentication server called a RADIUS server. This protocol is used widely in wired and wireless networks and operates at the data link layer of the OSI model.
The primary purpose of 802.1X authentication is to restrict access to the network from any sources that shouldn’t have it. With this technology, businesses may limit network access depending on the user’s or device’s credentials. Using this kind of authentication to enforce stringent access controls and block unauthorized access improves the safety of a network.
What Is MAC Authentication?
Generally, 802.1X authenticates users and devices through a combination of username and password or digital certificates. However, not all devices are capable of authenticating through these means.
This is when a device’s Media Access Control (MAC) address can come into play. Each device’s network interface card (NIC) has a media access control address. In most cases, this 48-bit number will seem like six sets of two hexadecimal digits, each group separated by a colon or a hyphen.
A MAC address can be used in lieu of or even with credentials or passwords for authentication. If you are doing 802.1X with MAC Authentication, a device’s MAC address is provided to an authentication server whenever it tries to connect. The server will only allow access after verifying that the client’s MAC address is on the approved list.
RADIUS Server and MAC Authentication Bypass
A Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server is often used to authenticate users using MAC addresses. The AAA services provided by a network are centralized on the RADIUS server.
A MAC address and an authentication request from a device trying to join a network to the RADIUS server are sent. The server compares the MAC address to its list of authorized devices and grants or denies the network connection accordingly. The RADIUS server will provide an ACCESS_ACCEPT message if the MAC address checks out. However, if the MAC address has yet to be verified or authorized, an ACCESS_REJECT message is issued to the device, blocking access to the network.
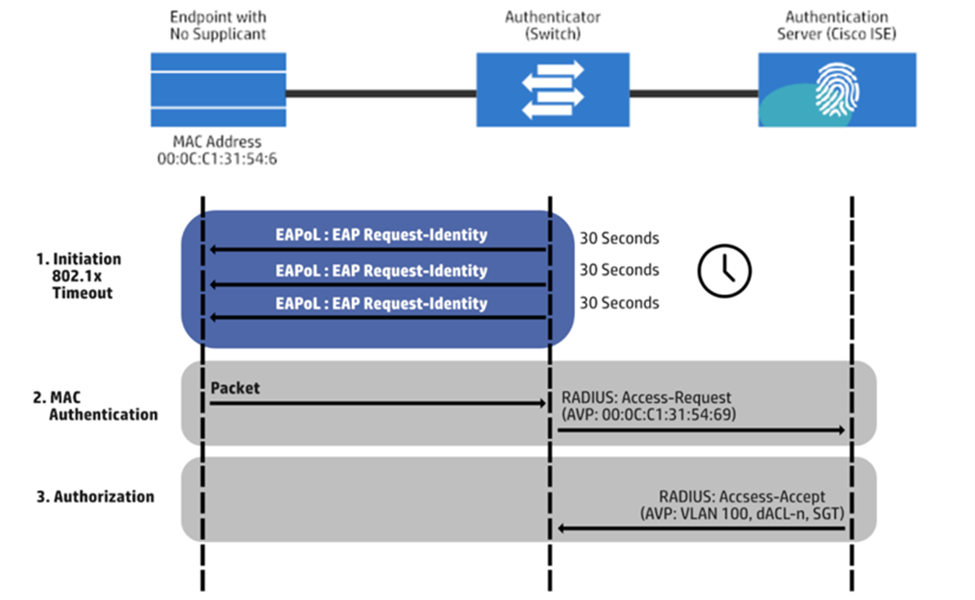
MAC authentication bypass is often used instead of 802.1X MAC authentication for devices that do not support it. Examples of devices that may not support 802.1X include medical devices, many gaming consoles, and some printers. Here is a list of devices that support 802.1X.
The MAC address alone is sufficient for these devices to establish a network connection. Thanks to this bypass technique, no additional credentials or certificates are required. The RADIUS server checks the MAC address, which, if correctly set up, may circumvent MAC authentication.
Benefits of MAC Authentication for Devices That Don’t Support 802.1X
There are several benefits, both in network security and device management, to using MAC authentication for devices lacking 802.1X functionality.
Segmentation of Devices Into Different VLANs
Policies may be set up during MAC-based RADIUS authentication configuration to partition networks depending on subsets of MAC addresses. Keeping unsecured IoT devices off of the same virtual local area network (VLAN) as servers housing private data or devices requiring a high level of authorization is crucial. The possibility of breaches and unauthorized access is reduced when these devices are kept in separate, secure locations.
Enhancing Security With Unique MAC Addresses
An important benefit of RADIUS MAC authentication is that it requires knowledge of the device’s unique MAC address and the network password. Unauthorized users will have more difficulty breaking into the network because of this extra safeguard.
Restricting Access to Specific MAC Addresses
With RADIUS MAC authentication, you may restrict network access to authorized MAC addresses. Businesses may restrict network access to just the necessary devices by compiling a list of approved MAC addresses. This further limits the attack surface and decreases the danger of unauthorized devices getting permits.
Implementing 802.1X MAC Authentication
Step-by-Step Process for 802.1X Wireless Authentication
The following is a step-by-step guide for organizations looking to deploy MAC authentication for devices that do not support 802.1X.
Set Up a RADIUS Server
Setting up a RADIUS server to manage requests for authentication from connected devices is the first order of business. The RADIUS server records the approved MAC addresses and functions as a central authentication authority.
Configure Network Infrastructure
The next step is to set up MAC address authentication on the network infrastructure devices like switches and access points. The RADIUS server’s IP address must be entered, and the network equipment’s authentication settings must be adjusted accordingly.
Define VLAN Segmentation
Organizations can set up virtual local area networks (VLANs) and assign unique MAC addresses to each VLAN to guarantee adequate network segmentation and security. This enables devices to be partitioned into distinct network sections according to their own security needs and the rules in place.
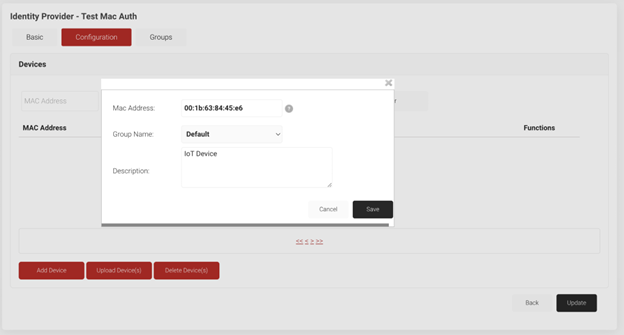
Enable MAC Authentication on Devices
You normally need to adhere to these procedures in order to configure devices for MAC authentication. The device’s distinctive MAC address may often be located in its network settings. The MAC address should then be entered into the appropriate network or security settings for MAC authentication by gaining access to the device’s configuration settings. The device will now utilize the MAC address for network authentication once you save the adjustments.
The device itself just requires a minimum amount of setup if you’re utilizing a RADIUS server for MAC authentication. The RADIUS server will handle the authentication procedure, so you’ll mostly need to make sure the device is configured to connect to the right SSID.
You may need to set up the device’s PSK and MAC authentication settings individually in certain circumstances when combining PSK and MAC authentication is possible. For instructions that are particular to your device, contact IT support or the device’s manual.
Test and Monitor
Once everything has been set up, rigorous testing of the MAC authentication procedure is required. This process includes connecting the devices to the network and checking that they have been authenticated and given the right level of network access based on their allocated VLAN.
Leveraging the RADIUS Server for MAC Authentication
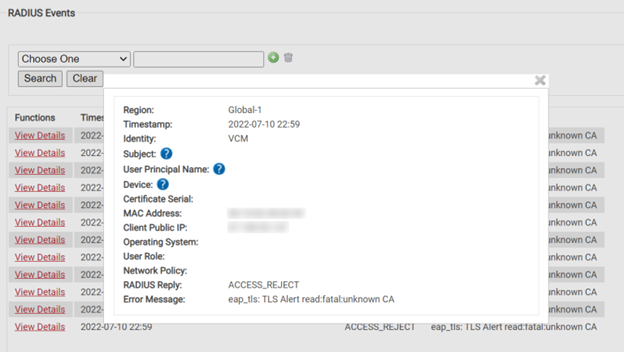
When it comes to 802.1X MAC authentication, the RADIUS server is essential. It processes authentication requests, checks the MAC addresses with a whitelist, and allows or disallows network access.
A RADIUS server can be used for MAC authentication to centralize the authentication process and apply uniform security rules throughout the network. Fine-grained control over which devices are permitted to join is possible thanks to additional capabilities like MAC address filtering that may be specified on the RADIUS server.
In addition, a RADIUS server provides auditing and logging features, helping businesses keep track of who is trying to access the network and whether they should be. This allows for preventative steps to be taken and improves network security in general.
Organizations can offer a safe network environment for devices that do not support 802.1X authentication by using MAC authentication and a RADIUS server. In addition to enhancing security and reducing the danger of unauthorized device connections, this method also enables fine-grained control over network access.
It’s worth noting that Cloud RADIUS may be used to install RADIUS server capabilities. Cloud RADIUS offers the benefits of quick implementation, scalability, and decreased infrastructure overhead. Cloud-based solutions remove the need for organizations to operate and maintain their own RADIUS servers, making them a more convenient and efficient option.
In conclusion, using a RADIUS server for MAC authentication provides centralized control, enhanced security, and granular access management. By choosing Cloud RADIUS solutions, organizations may further simplify their deployment and maintenance procedures while making use of a RADIUS server’s extensive functionality and logging capabilities.
Improving MAC Authentication With Customizable Attributes
With its customizable features, MAC authentication offers a safe mechanism for connecting non-802.1X-enabled devices to the network. A Cloud RADIUS option comes into play here:
Enhancing Security With MAB and Filtering
Organizations may design fine-grained access controls based on MAC addresses, device types, or other features with the help of a Cloud RADIUS solution that supports MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) and Filtering. This improves security since it restricts network access to approved gadgets only.
Adding Context to Authentication With Customizable Attributes
Customizable characteristics may be added to the authentication process using cloud RADIUS systems. Organizations may improve security by making more well-informed judgments regarding access control thanks to the extra information these properties provide about the device, user, or location.
Supporting MAB, Filtering, and Cloud RADIUS
In conclusion, protecting devices that can’t use WPA2-Enterprise is important to keep a network safe. Using the devices’ individual MAC addresses, MAC authentication provides a workable approach. Organizations may create stringent access restrictions, segregate devices into VLANs, and reduce the risks associated with unauthorized network access by using MAC authentication and a RADIUS server.
When it comes to MAC authentication, SecureW2 has you covered. Our solution guarantees that only permitted devices may connect by supporting MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) and Filtering. Our Cloud RADIUS further improves MAB’s security by letting you specify additional characteristics to use as authentication context.
Get in touch with us today to find out how SecureW2 can improve your network’s safety.