LDAP Vs. RADIUS
Two widely used protocols, LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) and RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) are essential to network authentication and access management. These protocols are the crucial building pieces that allow for effective and safe user management in a networked setting. LDAP is especially good at handling user IDs and associated attributes since it was created for directory services, making organizing and retrieving data in a hierarchical structure easier. Conversely, RADIUS focuses on offering a centralized framework for authentication and authorization; it is frequently used in networking situations like Wi-Fi security and remote access.
This article walks administrators through selecting the best solution for their network requirements by exploring LDAP and RADIUS’s unique features and relative strengths. Understanding the complexities of these protocols is critical for creating strong and secure authentication processes inside organizational infrastructures.
What is LDAP?
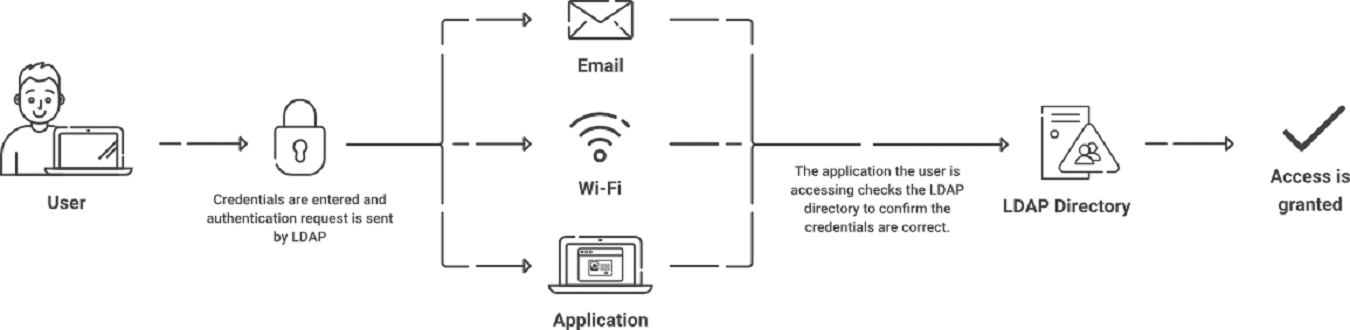
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, or LDAP, is a software protocol that enables an entity to look up data stored on a server. The “data” can be information about organizations, devices, or users stored in directories. LDAP is the protocol used by servers to speak with on-premise directories.
Data is stored in a hierarchical structure called a Directory Information Tree (DIT), which organizes data into a branching “tree” structure, making it easier for admins to navigate their directories, find specific data, and administer user access policies.
How Does the LDAP Protocol Work?
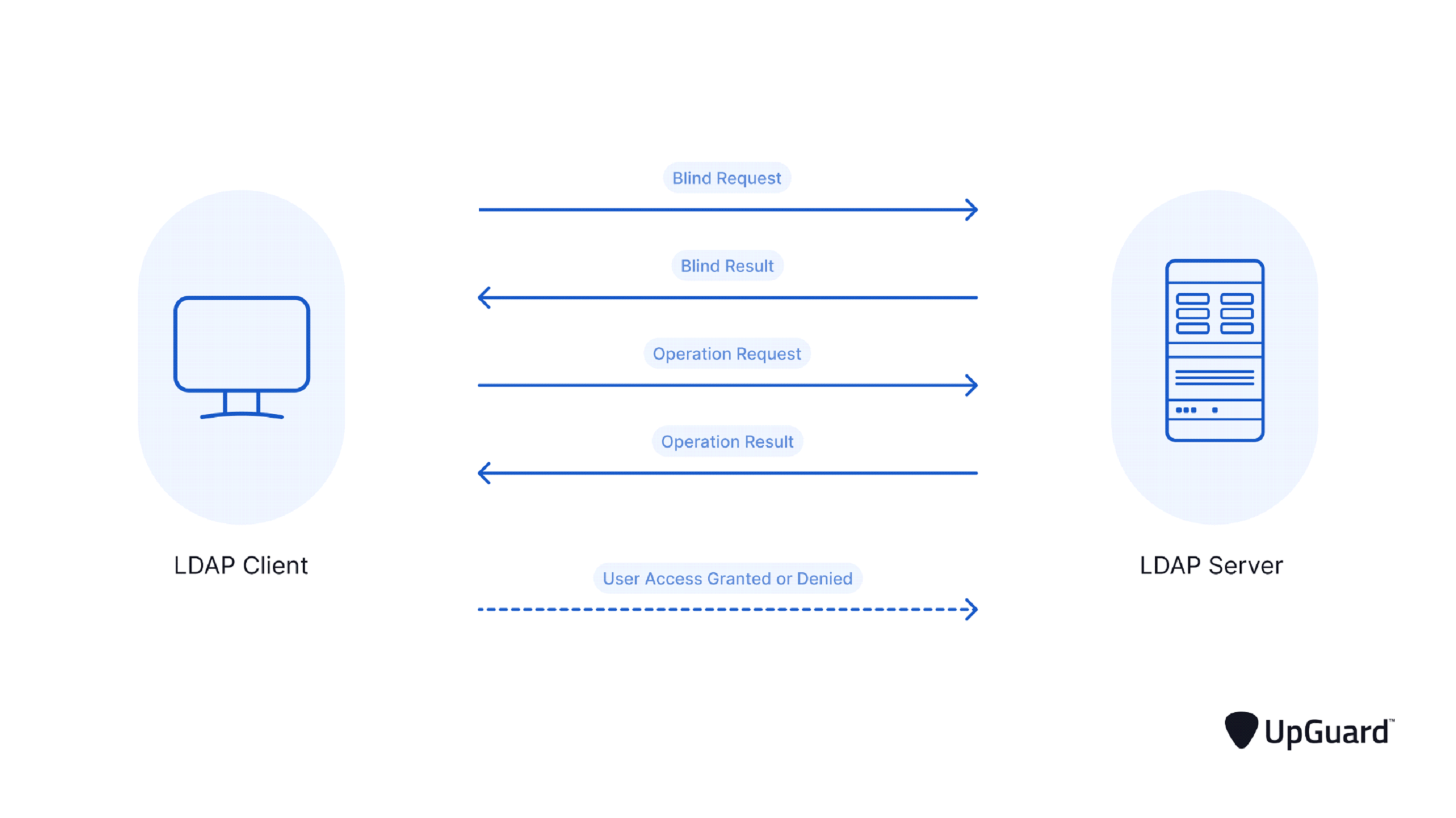
Briefly put, the LDAP client delivers the user credentials entered into the LDAP server to authenticate the user. Once these credentials have been verified against the information in the directory service, the server decides whether to approve or deny the user’s request to log in.
Why is LDAP Important?
Given the growing number of risks to credentials, including increasingly sophisticated attack vectors, it’s important to protect them in any way possible and prevent hackers from gaining access to vital resources. That is one of the issues LDAP helps safeguard against. It achieves the following:
⦁ LDAP secures your passwords
⦁ LDAP Verifies the Identity of the Requester Who Asks for Private Information
⦁ LDAP Deletes Sensitive Information When It Is No Longer Needed
⦁ LDAP Backs Up Critical Files
LDAP is mostly used for credential storage, i.e., usernames and passwords. It does, however, also offer a large number of additional services and apps that verify the users. One example is validating user data with Docker, Jenkins, and Kubernetes through LDAP authentication. LDAP also uses servers and various system administrators to keep an environment safe within the company.
The function of LDAP is also evident in other applications and the binding of various operations that assist LDAP in the deletion of different entries or the search and comparison of them with other commands. Additionally, it aids in unbinding operations, entry extension, and alteration of already-existing entries.
Risks of the LDAP Authentication Protocol
Cybersecurity risks are associated with LDAP since it makes connecting to private network resources easier, and hackers have discovered vulnerabilities in LDAP authentication over time. LDAP injections are the most serious of these vulnerabilities.
An LDAP injection is a cyberattack in which private data stored in LDAP directories are accessed by injecting code into a web application. To accomplish harmful goals, the injected malware incorporates LDAP metacharacters that alter valid requests from LDAP clients. An LDAP injection may lead to an account takeover, user privilege escalation, or data breach. When the authentication server fails to verify the authenticity of LDAP client queries, cyberattackers can freely interact with LDAP, possibly leading to LDAP injections.
Is LDAP an AAA Server?
In network security, AAA stands for authentication, authorization, and accounting. This nickname is often applied to RADIUS servers because they perform all the aforementioned functions.
An LDAP server can perform similar functions so that you can call a properly configured LDAP server by the same name. However, the problem with LDAP servers is that they require on-premise hardware, sharply limiting their scalability. Additionally, LDAP is restricted to credential-based authentication, which isn’t the most secure authentication method today.
An AAA server is a crucial component of WPA2-Enterprise, also known as the 802.1X standard. AAA servers are specifically designed for network authentication, and LDAP servers alone cannot authenticate users on Wi-Fi. Thus, while they can perform many of the functions of AAA servers, they are inherently inferior to other options like RADIUS.
What is RADIUS?
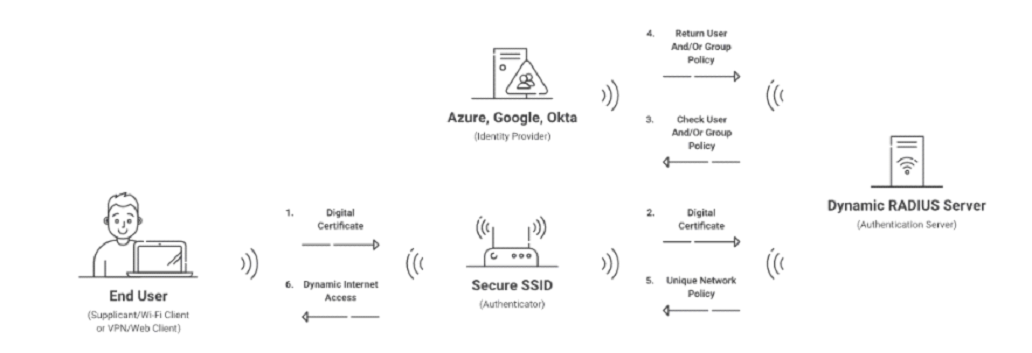
A RADIUS, or the Remote Access Dial-In User Service, is to authenticate the user and their device and authorize them for network access. The authorization and authentication process occurs each time a user re-connects to the network, taking the guesswork out of determining who is using your network.
Using a RADIUS is an effective way to boost network security and visibility. RADIUS can authenticate credentials, OTP, and hardware security keys and is especially effective when configured properly with certificates, which we will delve into in the next section.
How Does the RADIUS Protocol Work?
In summary, to authenticate a user:
A RADIUS client notifies the RADIUS server via a RADIUS Access-Request message. The Access-Request message contains the user credentials. The RADIUS server receives the request, checks the credentials against the user database, and then sends back one of three replies in response:
Access-Accept: Approves the user’s attempt to log in.
Access-Reject: Dismisses the user’s attempt to log in.
Access-challenge: Provides the user with an additional challenge, such as requesting a code entry.
RADIUS enables accounting in addition to authentication and authorization.
Differences Between RADIUS and LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
Here are some of the major differences in RADIUS vs LDAP –
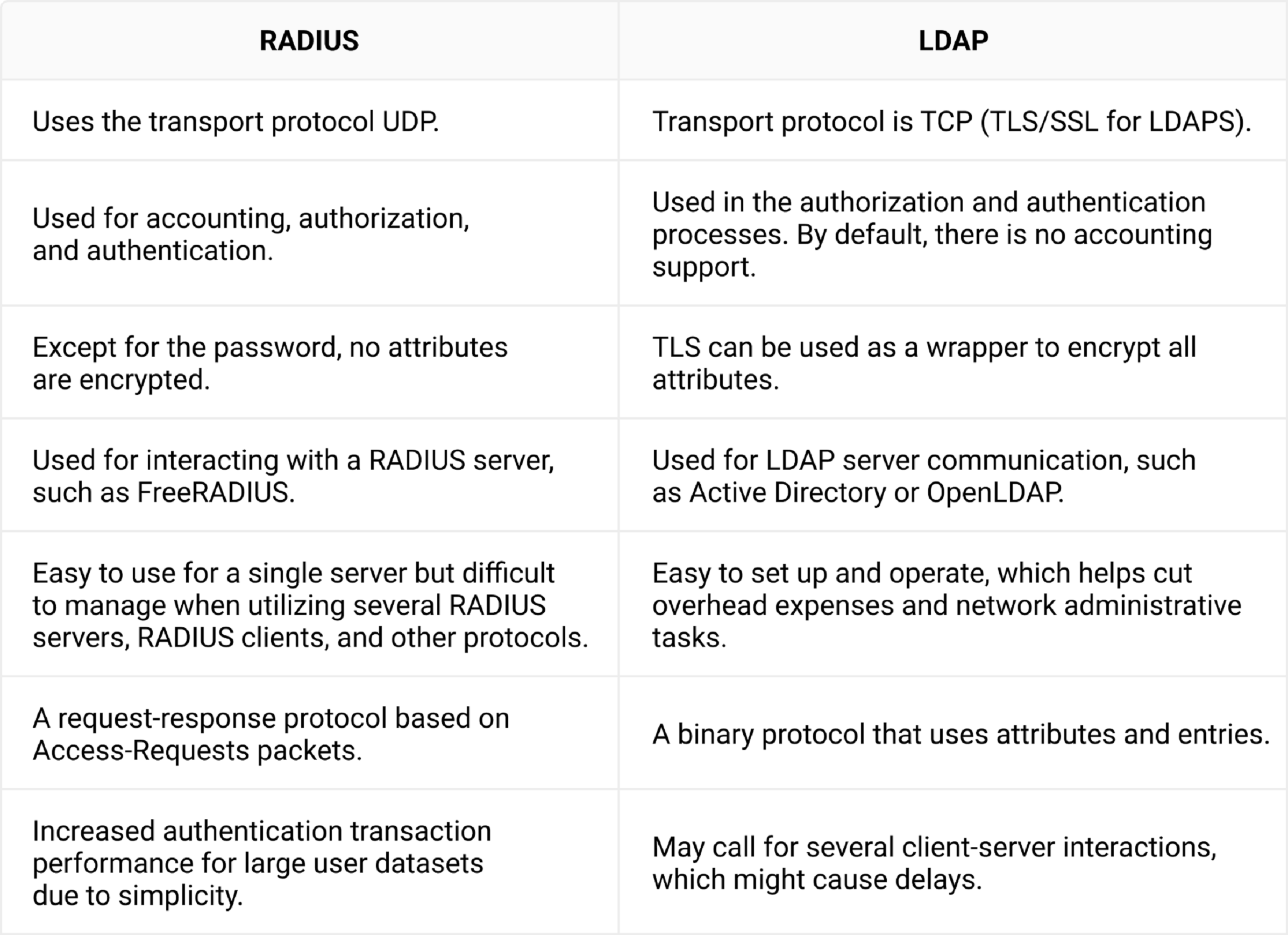
A Comparative Analysis of RADIUS vs. LDAP in Network Security
LDAP and RADIUS are authentication protocols that enable users to access their organization’s resources. It’s important to clarify that RADIUS and LDAP authentication are not the same thing, and there are substantial differences in how either works.
For example, LDAP relies exclusively on unsecured credentials, and with 10 million attacks targeting usernames and passwords occurring every day, it’s safe to say the usability and security flaws of credentials have accelerated. Not to mention many organizations are unsatisfied with credentials as authentication protection for their network due to IT help desk tickets and password sharing.
Another security vulnerability in LDAP is they don’t necessarily have a way to protect users from accidentally connecting to the wrong server. Cyber attacks prey on users by setting up false access points and encouraging people to connect.
Using RADIUS allows for a key security mechanism: server certificate validation. This guarantees that the user only connects to the network they intend to by configuring their device to confirm the identity of the RADIUS by checking the server certificate. If the server certificate is not the one the device is looking for, it will not send a certificate or credentials for authentication. This prevents users from falling victim to various network attacks, such as a Man-in-the-Middle attack.
However, one of the greatest security vulnerabilities of LDAP is that they are generally on-premise. Not only does this make them costly to maintain, but it exposes them to a unique range of threats that cloud-hosted infrastructure doesn’t have to contend with. Such threats include power outages, severe weather, fire, and bad actors on-site. If you don’t house the LDAP server in a safe location, it’s possible that simple employee negligence could damage it, too.
It’s easy to see that RADIUS is superior to LDAP regarding network security. But how do they compare when it comes to authentication processes?
Authentication Dynamics: RADIUS vs LDAP
Another one of LDAP’s greatest flaws is that it’s generally confined to credential-based authentication, as discussed previously. It’s typically used to verify someone’s username and password, which are elements that can be easily stolen.
On the other hand, RADIUS is not limited to only one authentication method; RADIUS can use multiple factors of authentication (MFA) to provide greater protection than any single method.
A RADIUS server can also be paired with a PKI, like SecureW2’s managed PKI, to authenticate digital certificates issued to end users. This makes RADIUS essential for Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), as you can ensure that each device on your network should have access.
An important thing to note is that, unlike LDAP, a RADIUS server does not store user and device information. It needs an Identity Provider (IDP) to function properly. IDPs are directories of user information that tell the RADIUS who an individual is and what type of access is warranted based on their role in an organization.
Scalability in RADIUS Server vs. LDAP Server
Another difference between LDAP and RADIUS stems from the use of on-premise servers. While historically, both protocols relied on on-prem servers, RADIUS has evolved and can now be fully integrated into a cloud-based infrastructure. This is especially noteworthy due to the expenses associated with on-premise servers. These costs can be quite hefty, as they often demand at least some level of maintenance by a skilled professional, on-site security, and setup costs. Furthermore, cloud environments offer stronger data protection, easy access to authorized users, and greater control over who has data access.
Put simply, RADIUS and LDAP are two authentication protocols. Although they have their differences, they aren’t mutually exclusive. It is certainly possible to use both at the same time.
While RADIUS-backed, certificate-based authentication does not require LDAP, they have often been combined to enable Identity Lookup. Identity Lookup validates that a user is active within the organization during authentication by checking the identifying information against a user list. This solution is helpful but cannot make the transition to a cloud-based network.
One common instance of RADIUS working with LDAP occurs when an organization uses LDAP directories as its Identity Provider. Microsoft Active Directory is a popular example of an LDAP-backed directory often used as an IDP. Our own Cloud RADIUS can work in this scenario with our turnkey-managed PKI to provide secure, certificate-based authentication to organizations using Active Directory.
As we mentioned above, the flaw with this setup is that it relies upon on-premise hardware. If you’re looking to transition to a future-viable cloud environment, though, SecureW2 has a solution for you.
Can RADIUS Use LDAP?
Put simply, RADIUS and LDAP are two authentication protocols. Although they have their differences, they aren’t mutually exclusive. It is certainly possible to use both at the same time.
While RADIUS-backed, certificate-based authentication does not require LDAP, they have often been combined to enable Identity Lookup. Identity Lookup validates that a user is active within the organization during authentication by checking the identifying information against a user list. This solution is helpful but cannot make the transition to a cloud-based network.
One common instance of RADIUS working with LDAP occurs when an organization uses LDAP directories as its Identity Provider. Microsoft Active Directory is a popular example of an LDAP-backed directory often used as an IDP. Our own Cloud RADIUS can work in this scenario with our turnkey-managed PKI to provide secure, certificate-based authentication to organizations using Active Directory.
As we mentioned above, the flaw with this setup is that it relies upon on-premise hardware. If you’re looking to transition to a future-viable cloud environment, though, SecureW2 has a solution for you.
A Cloud-Driven Conclusion to LDAP vs. RADIUS
Although LDAP has shown to be a dependable protocol for credential-based authentication, its intrinsic drawbacks highlight the need for a more flexible solution, particularly when it comes to password security and on-premise infrastructure. SecureW2 has worked with hundreds of organizations looking to move past LDAP, providing certificate-based authentication and an identity lookup feature that is distinctive to the market for SAML-based cloud directories. Through a smooth integration with Cloud RADIUS,
SecureW2 releases enterprises from the limitations of on-premise LDAP architecture while improving network security. This change guarantees a more simplified and effective identity lookup procedure advantageous to IT staff and end users.
Contact us now to start your journey towards safe, future-ready authentication.